Toyota Corolla Cross: On-vehicle Inspection
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION
CAUTION / NOTICE / HINT
HINT:
- Steps 2 to 9 specify the procedure to determine the cause of a refrigerant leak.
- Step 10 specifies the procedure to check if there is a clog in the expansion valve.
PROCEDURE
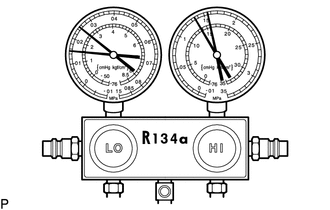
1. INSPECT REFRIGERANT PRESSURE WITH MANIFOLD GAUGE SET
HINT:
The following examples show the readings of a manifold gauge set and the corresponding air conditioning system problems.
(a) Read the manifold gauge pressure when the following conditions are met:
- Doors are fully open.
- The engine is idling.
- The A/C switch is on.
- The temperature is set to max cool.
- The blower speed is set to high.
- Temperature at the air inlet with recirculate selected is 30 to 35°C (86 to 95°F).
| (1) Normally functioning air conditioning system Gauge Reading
|
|
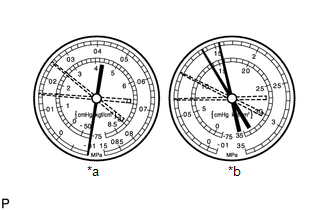
(2) Abnormally functioning air conditioning system
- During operation, pressure on low pressure side cycles between normal and vacuum
*a
LO
*b
HI
Symptom
Air conditioning system periodically cools and then fails to cool
Probable Cause
Moisture in air conditioning system freezes at expansion valve orifice, causing refrigerant to temporarily stop circulating
After system stops and warms up again, ice melts and normal operation is temporarily restored
Diagnosis
Cooler dryer (integrated into condenser tank) saturated with moisture
Moisture in air conditioning system is freezing at expansion valve orifice and blocking circulation of refrigerant
Corrective Actions
Replace cooler dryer
Remove moisture by repeatedly evacuating air from air conditioning system
Recharge air conditioning system with proper amount of new or purified refrigerant
HINT:
For the example above, moisture is present in the air conditioning system.
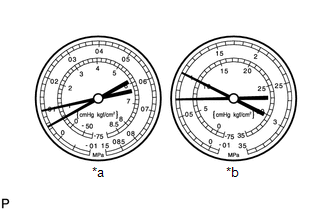
- Pressure is low on both low and high pressure sides
*a
LO
*b
HI
Symptom
Air conditioning system does not cool effectively
Insufficient cooling performance
Probable Cause
Refrigerant leaks from air conditioning system
Diagnosis
Insufficient refrigerant
Refrigerant leaking
Corrective Actions
Check for refrigerant leaks and repair if necessary
Recharge air conditioning system with proper amount of new or purified refrigerant
If gauges indicate pressure of close to 0, then it is necessary to evacuate air conditioning system after repairing leaks
HINT:
For the example above, there is insufficient refrigerant.
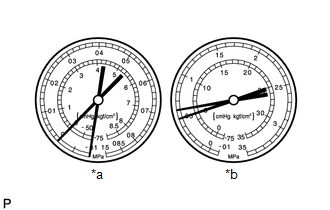
- Pressure is low on both low and high pressure sides
*a
LO
*b
HI
Symptom
Air conditioning system does not cool effectively
Frost exists on pipe from condenser to evaporator unit
Probable Cause
Refrigerant flow is obstructed by dirt inside pipes of condenser core
Diagnosis
Condenser is clogged
Corrective Actions
Replace condenser
HINT:
For the example above, there is poor circulation of refrigerant.
- Vacuum is indicated on low pressure side and very low pressure is indicated on high pressure side
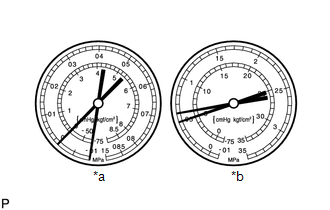
*a
LO
*b
HI
Symptom
Air conditioning system does not cool effectively (system may cool occasionally)
Frost or condensation is seen on piping on both sides of receiver/dryer or expansion valve
Probable Cause
Refrigerant flow is obstructed by moisture or dirt in air conditioning system
Expansion valve is stuck closed
Diagnosis
Refrigerant does not circulate
Corrective Actions
Replace expansion valve
Replace condenser
Evacuate air conditioning system and recharge with proper amount of new or purified refrigerant
HINT:
For the example above, the refrigerant does not circulate.
- Pressure is too high on both low and high pressure sides
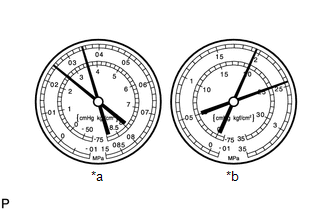
*a
LO
*b
HI
Symptom
Air conditioning system does not cool effectively
Probable Cause
Unable to provide sufficient performance due to excessive amount of refrigerant
Cooling effectiveness of condenser is insufficient
Diagnosis
Excessive amount of refrigerant in air conditioning system because excessive refrigerant was added during recharging
Cooling effectiveness of condenser is insufficient because condenser fins are clogged or cooling fan is faulty
Corrective Actions
Clean condenser
Check operation of condenser cooling fan
If condenser is clean and fan operation is normal, check amount of refrigerant and recharge air conditioning system with proper amount of new or purified refrigerant
HINT:
For the example above, the air conditioning system is overcharged or cooling effectiveness of condenser is insufficient.
- Pressure is too high on both low and high pressure sides
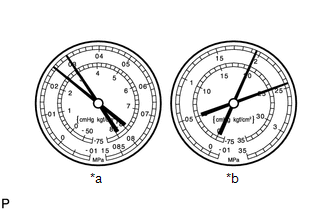
*a
LO
*b
HI
Symptom
Air conditioning system does not cool
The low pressure piping is too hot to touch
Probable Cause
Air in air conditioning system
Diagnosis
Air present in air conditioning system
Insufficient vacuum purging when evacuating air conditioning system
Corrective Actions
Replace cooler dryer
Check compressor oil to see if it is dirty or insufficient
Evacuate air conditioning system and recharge it with new or purified refrigerant
NOTICE:
These gauge indications occur when the air conditioning system has been left open and then recharged without evacuating the system.
HINT:
For the example above, air is present in the air conditioning system.
- Pressure is too high on both low and high pressure sides
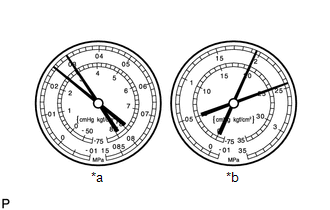
*a
LO
*b
HI
Symptom
Air conditioning system does not cool effectively
Frost or large amount of condensation on piping on low pressure side
Probable Cause
Expansion valve may be stuck open or metering refrigerant incorrectly
Diagnosis
Excessive refrigerant in low pressure piping
Expansion valve open too wide
Corrective Actions
Replace expansion valve
HINT:
For the example above, there is an expansion valve malfunction.
- Pressure is too high on both low and high pressure sides or pressure is too low on high pressure side
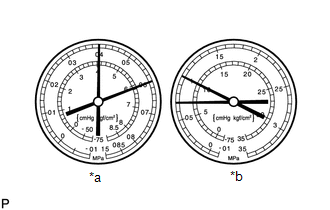
*a
LO
*b
HI
Symptom
Air conditioning system does not cool effectively
Probable Cause
Internal leak in compressor
Diagnosis
Low compression
Leak from damaged valve or other compressor component
Corrective Actions
Replace compressor
HINT:
For the example above, there is insufficient compressor compression.
(3) Gauge readings (Reference)
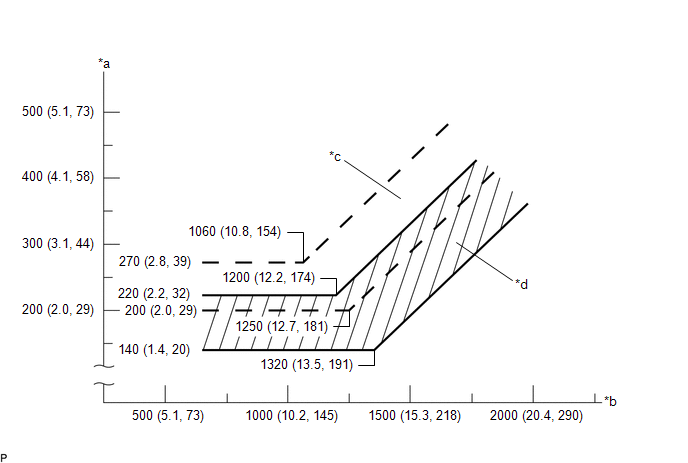
|
*a | Pressure on Low Pressure Side kPa (kgf/cm2, psi) |
*b | Pressure on High Pressure Side kPa (kgf/cm2, psi) |
|
*c | Blower High Zone |
*d | Blower Low Zone |
2. INSPECT LEAK INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
The following inspection specifies how to determine the cause of a refrigerant leak after determining the location of the leak using a gas leak detector. Use this procedure to determine where to clean and what to be replaced. Illustrations, specifications and part names are for reference only and may differ from the actual vehicle.
(a) Use a gas leak detector to inspect for refrigerant gas leaks.
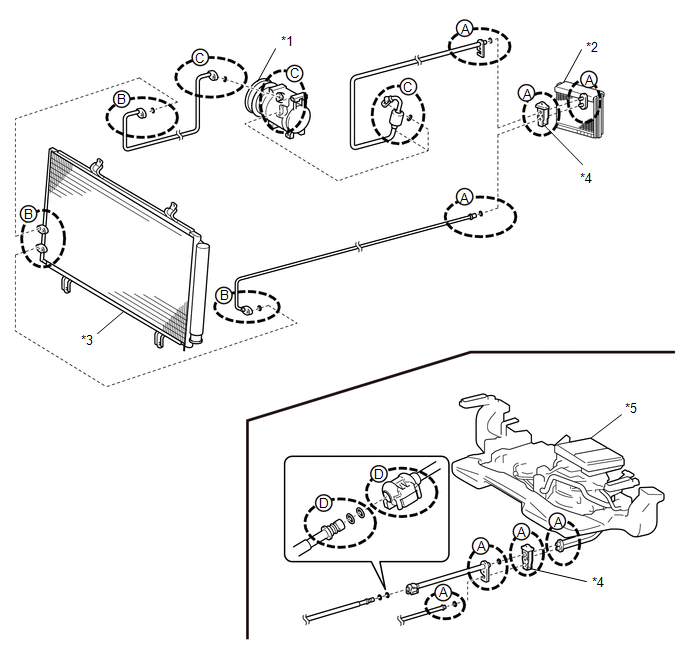
|
*1 | Compressor |
*2 | Evaporator |
|
*3 | Condenser |
*4 | Expansion Valve |
|
*5 | Rear Air Conditioning Unit |
- | - |
- When leaking occurs around "A" parts in the illustration:
Click here
.gif)
- When leaking occurs around "B" parts in the illustration:
Click here
.gif)
- When leaking occurs around "C" parts in the illustration:
Click here
.gif)
- When leaking occurs around "D" parts in the illustration:
Click here
.gif)
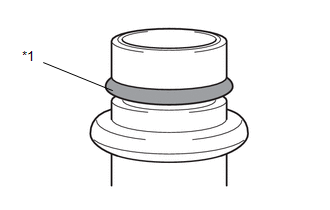
3. INSPECT EXPANSION VALVE AND PIPE FITTING AREA
NOTICE:
- Do not reuse the O-rings once they are removed.
- Make sure to complete the steps from a to h and replace all the parts in which defects are found.
- If all the related parts are normal, foreign material may be temporarily adhering to the O-ring or there may be an airtight malfunction due to deformation.
| (a) REMOVE PIPE: NOTICE:
(1) Remove the pipe from the expansion valve. |
|
| (b) CHECK O-RING SURFACE IN PIPE: NOTICE:
(1) Check the entire O-ring surface and make sure that it is free from defects, such as damage (cuts, dents or crushed areas), foreign material adhesion or twists. If there is any defect, clean or replace the part. Click here |
|
| (c) CHECK SEALING FACE OF PIPE: NOTICE: When removing the O-ring, use soft tools (such as tooth picks) to avoid damaging the sealing face or O-ring. (1) Remove the O-ring. (2) Check the entire pipe surface and make sure that it is free from defects, such as foreign material adhesion, damage or corrosion. If there is any defect, clean or replace the part. Click here |
|
| (d) CHECK SEALING FACE OF EXPANSION VALVE (PIPE SIDE): NOTICE: When it is difficult to check the surface condition due to oil adhesion, degrease the surface (such as by wiping it with a clean white cloth). Make sure not to lose any foreign material that was adhering to the surface. (1) Check the entire sealing face of expansion valve (pipe side) and make sure that it is free from defects, such as foreign material adhesion, damage or corrosion. If there is any defect, clean or replace the part. Click here |
|
| (e) REMOVE EXPANSION VALVE: NOTICE:
(1) Remove the expansion valve from the evaporator. HINT: If necessary, remove the air conditioning unit. Click here
|
|
| (f) CHECK SEALING FACE OF EXPANSION VALVE (EVAPORATOR SIDE): NOTICE: When it is difficult to check the surface condition due to oil adhesion, degrease the surface (such as by wiping it with a clean white cloth). Make sure not to lose any foreign material that was adhering to the surface. (1) Check the entire sealing face of expansion valve (evaporator side) and make sure that it is free from defects, such as foreign material adhesion, damage or corrosion. If there is any defect, clean or replace the part. Click here |
|
| (g) CHECK O-RING SURFACE IN EVAPORATOR: NOTICE:
(1) Check the entire O-ring surface and make sure that it is free from defects, such as damage (cuts, dents or crushed areas), foreign material adhesion or twists. If there is any defect, clean or replace the part. Click here |
|
| (h) CHECK SEALING FACE OF EVAPORATOR: NOTICE: When removing the O-ring, use soft tools (such as tooth picks) to avoid damaging the sealing face or O-ring. (1) Remove the O-ring. (2) Check the entire evaporator surface and make sure that it is free from defects, such as foreign material adhesion, damage or corrosion. If there is any defect, clean or replace the part. Click here |
|
4. INSPECT CONDENSER AND PIPE FITTING AREA
NOTICE:
- Do not reuse the O-rings once they are removed.
- Make sure to complete the steps from a to d and replace all the parts in which defects are found.
- If all the related parts are normal, foreign material may be temporarily adhering to the O-ring or there may be an airtight malfunction due to deformation.
| (a) REMOVE PIPE: NOTICE:
(1) Remove the pipes from the condenser. |
|
| (b) CHECK O-RING SURFACE IN PIPE: NOTICE:
(1) Check the entire O-ring surface and make sure that it is free from defects, such as damage (cuts, dents or crushed areas), foreign material adhesion or twists. If there is any defect, clean or replace the part. Click here |
|
| (c) CHECK SEALING FACE OF PIPE: NOTICE: When removing the O-ring, use soft tools (such as tooth picks) to avoid damaging the sealing face or O-ring. (1) Remove the O-ring. (2) Check the entire pipe surface and make sure that it is free from defects, such as foreign material adhesion, damage or corrosion. If there is any defect, clean or replace the part. Click here |
|
| (d) CHECK SEALING FACE OF CONDENSER: NOTICE: When it is difficult to check the surface condition due to oil adhesion, degrease the surface (such as by wiping it with a clean white cloth). Make sure not to lose any foreign material that was adhering to the surface. (1) Check the entire sealing face of condenser and make sure that it is free from defects, such as foreign material adhesion, damage or corrosion. If there is any defect, clean or replace the part. Click here |
|
5. INSPECT COMPRESSOR AND PIPE FITTING AREA
NOTICE:
- Do not reuse the O-rings once they are removed.
- Make sure to complete the steps from a to d and replace all the parts in which defects are found.
- If all the related parts are normal, foreign material may be temporarily adhering to the O-ring or there may be an airtight malfunction due to deformation.
| (a) REMOVE PIPE: NOTICE:
(1) Remove the pipes from the compressor. |
|
| (b) CHECK O-RING SURFACE IN PIPE: NOTICE:
(1) Check the entire O-ring surface and make sure that it is free from defects, such as damage (cuts, dents or crushed areas), foreign material adhesion or twists. If there is any defect, clean or replace the part. Click here |
|
| (c) CHECK SEALING FACE OF PIPE: NOTICE: When removing the O-ring, use soft tools (such as tooth picks) to avoid damaging the sealing face or O-ring. (1) Remove the O-ring. (2) Check the entire pipe surface and make sure that it is free from defects, such as foreign material adhesion, damage or corrosion. If there is any defect, clean or replace the part. Click here |
|
| (d) CHECK SEALING FACE OF COMPRESSOR: NOTICE: When it is difficult to check the surface condition due to oil adhesion, degrease the surface (such as by wiping it with a clean white cloth). Make sure not to lose any foreign material that was adhering to the surface. (1) Check the entire sealing face of compressor and make sure that it is free from defects, such as foreign material adhesion, damage or corrosion. If there is any defect, clean or replace the part. Click here |
|
6. INSPECT OTHER AREA
NOTICE:
- Do not reuse the O-rings once they are removed.
- Make sure to check all the related parts and replace all the parts in which defects are found.
- If all the related parts are normal, foreign material may be temporarily adhering to the O-ring or there may be an airtight malfunction due to deformation.
- Check the following parts. Refer to other procedures for details.
(a) CHECK OTHER PART:
NOTICE:
- Be sure there is sufficient light when checking the O-ring.
- If the condition of the surface is difficult to see, degrease it so it is easier to see. However, be careful when degreasing it so that any foreign matter that is attached to it is not misplaced.
| (1) Check the O-ring surface of the pipe or part. Click here |
|
| (2) Check the sealing face of the pipe. Click here
|
|
| (3) Check the sealing face of the part. Click here
|
|
7. INSPECT O-RING ABNORMALITY
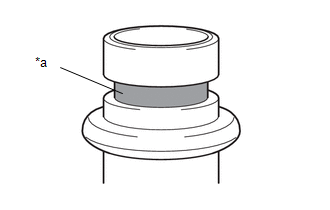
(a) Check the O-ring for any abnormalities.
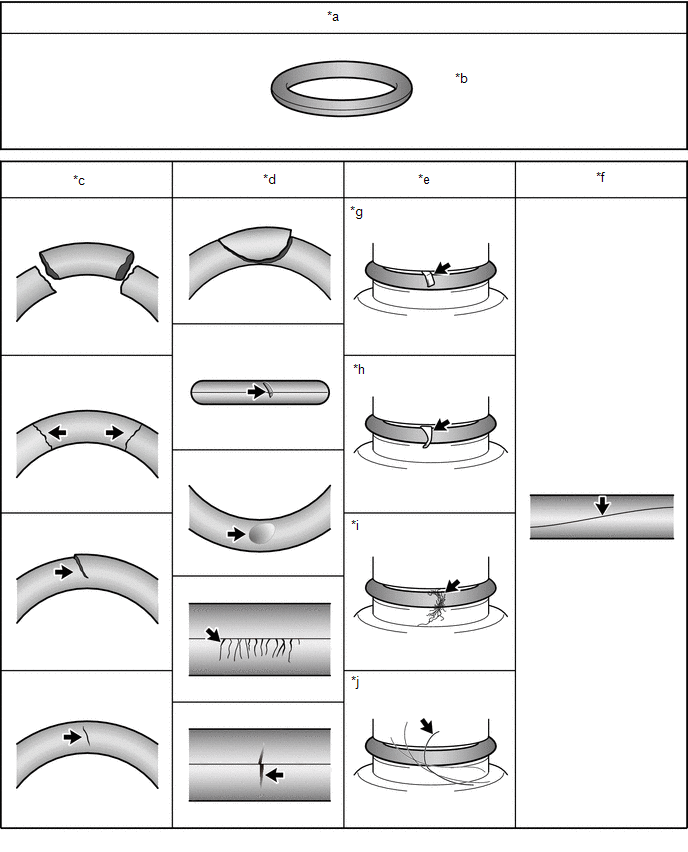
|
*a | OK condition |
*b | There are no cuts, dents, crushed areas, foreign material or twists |
|
*c | Cut |
*d | Dent/Crushed Area |
|
*e | Foreign Material |
*f | Twist |
|
*g | Metal fragment |
*h | Resin fragment |
|
*i | Lint |
*j | Hair |
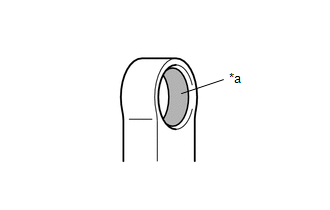
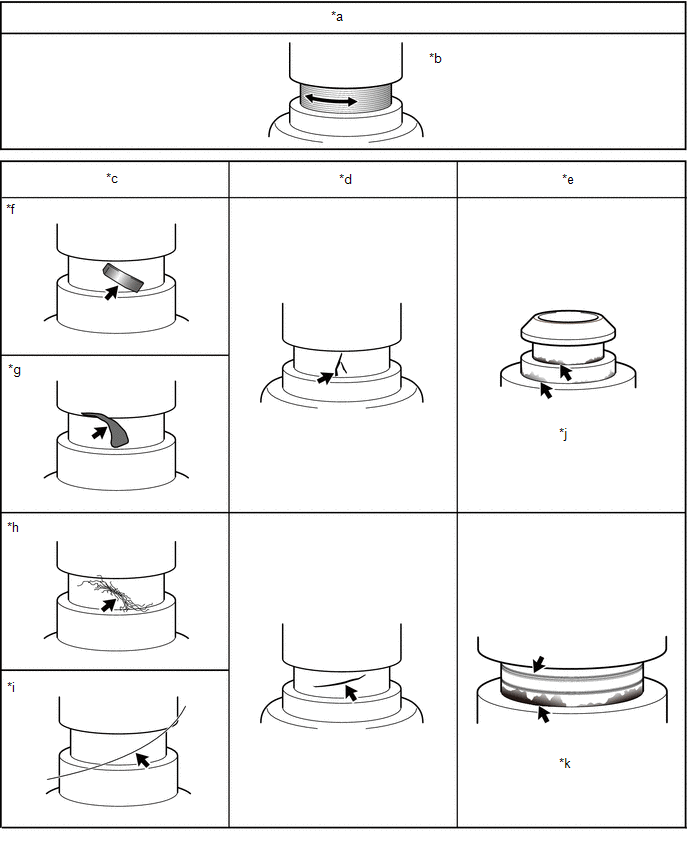
8. INSPECT SEALING FACE ABNORMALITY (O-RING ATTACHED AREA)
(a) Check the seal surface of the O-ring mount for any abnormalities.
|
*a | OK condition |
*b | Processing evidence in circumferential direction is NOT a cause of leakage. |
|
*c | Foreign Material |
*d | Damage |
|
*e | Corrosion |
*f | Metal fragment |
|
*g | Resin fragment |
*h | Lint |
|
*i | Hair |
*j | White and yellow materials adhered (corrosion product) |
|
*k | Damage (scratches) in axial direction and discoloration (black) |
- | - |
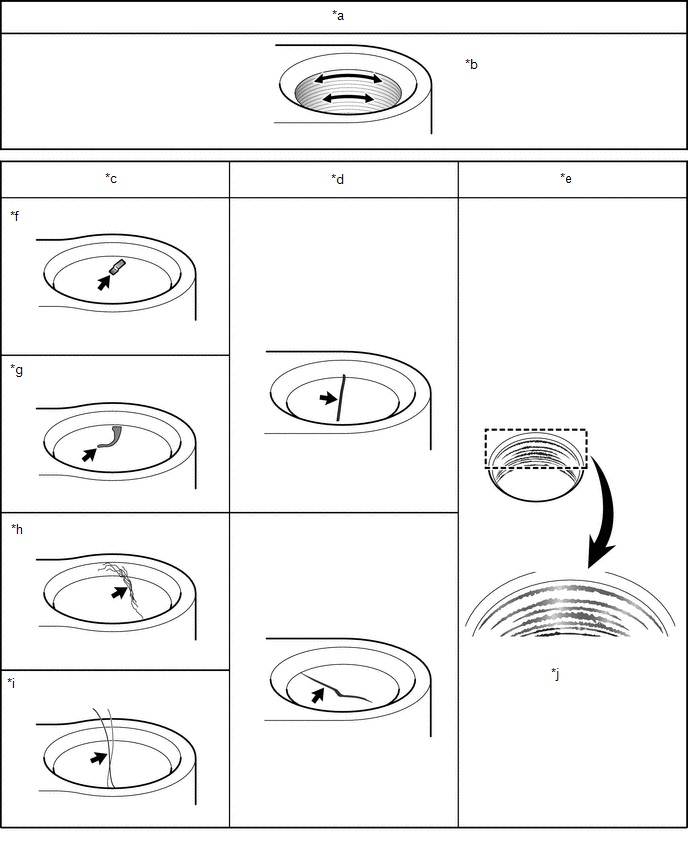
9. INSPECT SEALING FACE ABNORMALITY (PART JOINTED AREA)
(a) Check the seal surface of the connector for any abnormalities.
|
*a | OK condition |
*b | Processing evidence in circumferential direction is NOT a cause of leakage. |
|
*c | Foreign Material |
*d | Damage |
|
*e | Corrosion |
*f | Metal fragment |
|
*g | Resin fragment |
*h | Lint |
|
*i | Hair |
*j | Uneven discoloration (black) on sealing face |
10. INSPECT FOR FAULTY EXPANSION VALVE
(a) Recover refrigerant
(1) Connect the refrigerant recovery valve and recover the refrigerant.
NOTICE:
- Perform this procedure in accordance with the repair manual for each vehicle.
- Use the refrigerant recovery unit in accordance with the manufacturer's instruction manual.
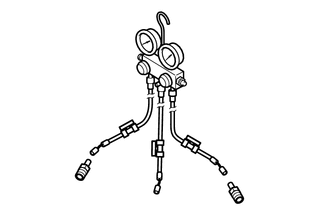
(b) Install air conditioner service tool set
| (1) Install the air conditioner service tool set to the vehicle (high pressure side). SST: 09985-20010 |
|
| (2) Open all the valves of the air conditioner service tool set. |
|
(3) Install the refrigerant recovery unit or vacuum pump to the vehicle (low pressure side).
Connection Conditions:|
Tool | Connected to |
|---|---|
|
Air conditioner service tool set (High pressure hose) |
Vehicle (High pressure side) |
|
Air conditioner service tool set (Center hose) |
- |
| Air conditioner service tool set (Low pressure hose) |
- |
| Refrigerant recovery unit or vacuum pump |
Vehicle (Low pressure side) |
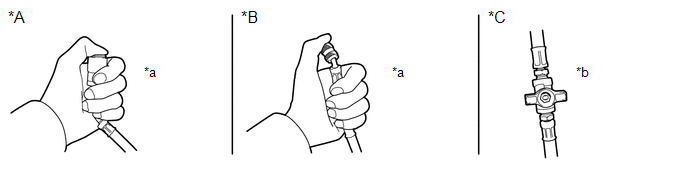
(c) Inspect expansion valve
(1) Depending on the type of low pressure side hose of the air conditioner service tool set, prevent air from being drawn in as shown in the illustration.
|
*A | With Attachment |
*B | Without Attachment |
|
*C | With Intermediate Valve |
- | - |
|
*a | Block the end of the hose with your thumb. |
*b | Close the intermediate valve. |
(2) While maintaining the above state, check that the gauge on the low pressure side changes when the center hose is closed and opened as shown in the illustration.
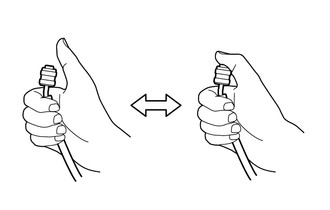 Result:
Result: |
Result | Judgement |
|---|---|
|
The gauge indicates a negative pressure (approximately -50 kPa (-0.5 kgf/cm2, -7.3 psi)). 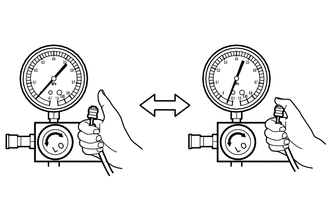 |
Expansion valve is normal. |
|
The indicated gauge pressure does not change. 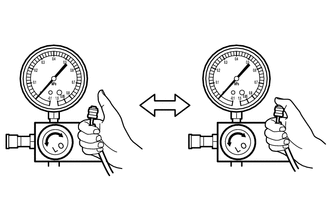 |
Expansion valve is abnormal. |