Toyota Corolla Cross: Diagnosis System
DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM
OBD II (except Mexico Models)
When troubleshooting OBD II (On-Board Diagnostics) vehicles, the GTS (complying with SAE J1978) must be connected to the DLC3 (Data Link Connector 3) of the vehicle. Various data in the vehicle's TCM (Transmission Control Module) can be then read.
OBD II regulations require that the vehicle's on-board computer illuminates the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Lamp) on the instrument panel when the computer detects a malfunction in:
- The emission control system and components.
- The powertrain control components (which affect vehicle emissions).
- The computer itself.
In addition, the applicable DTCs prescribed by SAE J2012 are stored in the TCM memory. If the malfunction does not recur in 3 consecutive trips, the MIL turns off automatically but the DTCs remain stored in the TCM memory.
To check the DTCs, connect the GTS to the DLC3. The GTS displays output DTCs, Freeze Frame Data, and a variety of engine data. The DTCs and Freeze Frame Data can be cleared with the GTS. In order to enhance OBD function on vehicles and develop the Off-Board diagnosis system, Controller Area Network (CAN) communication is used in this system. CAN is a network which uses a pair of data transmission lines spanning multiple computers and sensors. It allows for high speed communications between the systems and simplification of the wire harness connections.
EURO OBD (for Mexico Models)
When troubleshooting Europe On-Board Diagnostic (Euro-OBD) vehicles, the vehicle must be connected to an OBD scan tool (complying with ISO 15765-4).
Various data output from the vehicle's TCM can then be read.
Euro-OBD regulations require that the vehicle's on-board computer illuminate the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) on the instrument panel when the computer detects a malfunction in:
- The emission control system components.
- The powertrain control components which affect vehicle emissions.
- The computer
In addition, the applicable Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) prescribed by ISO 15765-4 are stored in the TCM memory. If the malfunction does not reoccur in 3 consecutive trips, the MIL turns off automatically but the DTCs remain stored in the TCM memory.
To check DTCs, connect the GTS or OBD scan tool to the Data Link Connector 3 (DLC3) of the vehicle.
The scan tool displays DTCs, the Freeze Frame Data and a variety of engine data.
The DTCs and Freeze Frame Data can be cleared using the scan tool.
Click here .gif)
.gif)
NORMAL MODE AND CHECK MODE (GTS Only)
(a) The diagnosis system operates in normal mode during normal vehicle use. In normal mode, 2-trip detection logic is used to ensure accurate detection of malfunctions. Check mode is also available to technicians as an option. In check mode, 1-trip detection logic is used when reproducing malfunction symptoms for increasing the ability of the system to detect malfunctions, including intermittent malfunctions.
2-TRIP DETECTION LOGIC
(a) When a malfunction is first detected, the malfunction is temporarily stored in the TCM memory (1st trip). If the same malfunction is detected during the subsequent driving cycle, the MIL is illuminated (2nd trip).
FREEZE FRAME DATA
(a) The TCM records vehicle and driving condition information as freeze frame data the moment a DTC is stored. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can be helpful in determining whether the vehicle was moving or stationary, whether the engine was warmed up or not and whether the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, as well as other data recorded at the time of a malfunction.
(b) The GTS displays freeze frame data recorded at five different points: 1) 3 times before the DTC is stored, 2) once when the DTC is stored, and 3) once after the DTC is stored. The data can be used to reproduce the vehicle condition around the time of the malfunction. The data may be helpful in determining the cause of a malfunction. It may also be helpful in determining whether a DTC is being caused by a temporary malfunction.
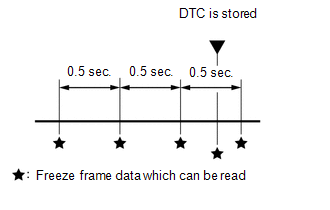
LIST OF FREEZE FRAME DATA
Powertrain > Transmission|
Tester Display |
|---|
|
Total Distance Traveled |
|
Total Distance Traveled - Unit |
|
Vehicle Speed |
|
Engine Speed |
|
Calculate Load |
|
Coolant Temperature |
|
Intake Air Temperature |
|
Ambient Temperature |
|
Engine Run Time |
|
Battery Voltage |
|
Glow Indicator Supported |
|
Throttle Position Sensor No.1 Voltage % |
|
Shift SW Status (Neutral) Supported |
|
Stop Light SW |
|
TC Terminal |
|
MIL ON Run Distance |
|
Running Time from MIL ON |
|
Time after DTC Cleared |
|
Distance from DTC Cleared |
|
Warmup Cycle Cleared DTC |
|
Accel Position from EFI |
|
NSS Sensor Speed |
|
NSS Sensor Voltage |
|
NO Sensor Speed |
|
NO Sensor Voltage |
|
NT Sensor Speed |
|
NC1 Sensor Speed |
|
NC1 Sensor Voltage |
|
Belt Clamping Force Sensor |
|
Shift SW Status (P Range) |
|
Shift SW Status (R Range) |
|
Shift SW Status (N Range) |
|
Shift SW Status (N,P Range) |
|
Shift SW Status (N,P Range) Supported |
|
Sport Shift Up SW |
|
Sport Shift Down SW |
|
Shift SW Status (S Range) |
|
Shift SW Status (D Range) |
|
A/T Oil Temperature No.1 |
|
ATF Thermal Degradation Estimate |
|
CVT Oil Press Calibration |
|
NT Sensor Voltage |
|
Synchronize Stroke Sensor Position |
|
Synchronize Stroke Sensor Voltage |
|
Status of Synchronize |
|
Lock Up Status |
|
CVT Shift Status Ratio |
|
Shift Mode |
|
Solenoid (SLU) |
|
Solenoid (SLS) High/Low |
|
Solenoid (SLS) MAX/MIN |
|
Solenoid (SLP) |
|
Solenoid (SLG) |
|
Solenoid (SL1) |
|
Solenoid (SL2) |
DATA LINK CONNECTOR 3 (DLC3)
(a) Check the DLC3.
Click here .gif)
AUXILIARY BATTERY VOLTAGE
Standard Voltage:
11 to 14 V
If the voltage is below 11 V, recharge or replace the auxiliary battery.
MIL (Malfunction Indicator Lamp)
(a) The MIL is illuminated when the ignition switch is turned to ON (with the engine not running).
If the MIL does not illuminate, check the MIL circuit.
Click here .gif)
(b) The MIL will turn off when the engine is started. If the MIL remains illuminated, the diagnosis system has detected a malfunction or abnormality in the system.


